Transfer of Upper Louisiana
Watercolor and pastel by F. L. Stoddard, no date. Courtesy Missouri History Museum, “Early St. Louis and the Transfer of Power.”
The transfer of Upper Louisiana occurred on 9 March 1804 and 10 March 1804.
Captain Amos Stoddard commanded an artillery company (approximately forty men) at Fort Kaskaskia in 1803. He and part of his company represented the United States in St. Louis in March 1804 when Spain transferred Upper Louisiana including St. Louis to France, which in turn transferred it to the United States a day later. He would then serve as the commandant of the Upper Louisiana Territory. Stoddard died in May 1813 from wounds received at the Battle of Fort Meigs in Ohio during the War of 1812.[1]Mark J. Wagner in Fort Kaskaskia citing Robert A. Stoddard, ed., The Autobiography Manuscript of Major Amos Stoddard (San Diego: Robert Stoddard Publishing, 2016), 48–51.
Selected Pages
January 19, 1803
News from Capt. Stoddard

Fort Fayette, PA Capt. Amos Stoddard writes a letter to Col. Henry Burbeck informing the latter that he has arrived at Pittsburgh and is awaiting further orders. Those orders would be connected to what would later become the Lewis and Clark Expedition.
February 19, 1803
Stoddard's orders


Washington, DC Captain Stoddard receives orders to pick up tools at Fort Fayette and proceed to Kaskaskia, and Thomas Jefferson criticizes Senator Ross’ attempt to raise a force to take New Orleans by force.
September 4, 1803
Leaky boats


Newell, WV The pirogue and canoe used to lighten the barge both spring leaks. They stop to repair the leaks and dry wet cargo.
November 29, 1803
Spanish obstruction


Fort Kaskaskia, IL The captains are selecting more soldiers and making decisions about their next steps. While at Fort Kaskaskia, they learn the Spanish Governor of Upper Louisiana intends to block the expedition.
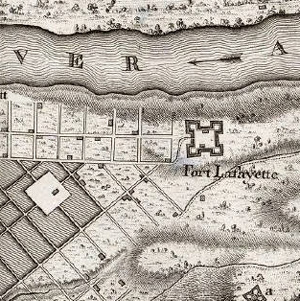
Fort Kaskaskia
Preliminary outpost
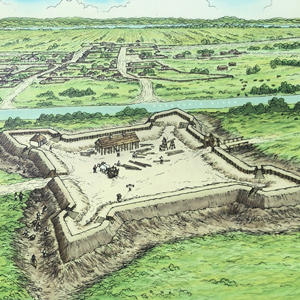

Archaeological investigations by the author and his students reveal the location of the American Fort Kaskaskia. Extracts from “Bound to the Western Waters: Searching for Lewis and Clark at Fort Kaskaskia, Illinois” by the lead archaeologist.
December 1, 1803
Kaskaskia recruits


Fort Kaskaskia, IL On or near this date, Clark and Lewis select new recruits. Lewis also writes a receipt to Amos Stoddard for 75 pounds of gunpowder and a cask.
January 2, 1804
Lewis's 'business of importance'


Winter Camp at Wood River, IL Clark receives papers from Lewis who is in Cahokia “on business of importance to the enterprise.” He learns that Captain Amos Stoddard will be the United States agent to receive the Louisiana Territory.
January 15, 1804
intoxicated helpers


Winter Camp at Wood River, IL In a letter to his brother-in-law, Clark describes his situation at Rivière à Dubois. Several men and a wagon, all loaded with whiskey, appear at camp.
February 19, 1804
New Spanish orders
Wood River Camp, IL On or near this date, the Spanish Lieutenant Governor Dehault Delassus receives orders to transfer the Upper Louisiana Territory to Captain Amos Stoddard.
February 24, 1804
"a great Dinner & porrade"


Winter Camp at Wood River, IL In St. Louis, Amos Stoddard and several citizens are told by Spanish Lt. Governor Dehault Delassus that he is ready to transfer Louisiana to the United States. A dinner and parade follow.
March 1, 1804
Orders for Sgt. Floyd


Wood River Camp, IL The day begins with sub-zero temperatures, and trouble brews when some of the enlisted men disobey Sgt. Ordway’s orders. In Washington City, Henry Dearborn orders Major Bruff to replace Amos Stoddard as military commander of Upper Louisiana.
March 8, 1804
Announcing Louisiana's transfer


Wood River Camp, IL Lewis is in Cahokia with Captain Amos Stoddard and his honor guard who are traveling to St. Louis to formally receive the Upper Louisiana Territory. Clark is likely already there.
March 9, 1804
Lowering the Spanish, raising the French


Wood River Camp, IL Lewis serves as a witness to the delivery and receipt of the Upper Louisiana from Spain to France. With speeches and ceremony, the Spanish flag is lowered, and the French flag is raised.
March 10, 1804
Lowering the French, raising the American
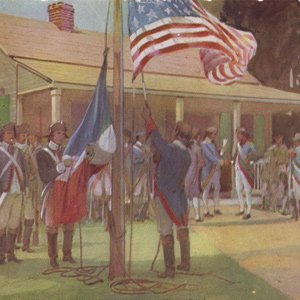

Winter Camp at Wood River, IL U.S. Army Captain Amos Stoddard, acting as the representative of France, declares Upper Louisiana as belonging to the United States. The French flag, flying for only one day, is lowered and the American flag raised.
April 7, 1804
Capt. Stoddard's ball


Clark, Lewis, and York travel to St. Louis to attend a formal dinner and ball hosted by Captain Amos Stoddard, new Commandant of Upper Louisiana. Sgt. Ordway is left in charge at Camp River Dubois.
April 8, 1804
Stoddard's expenses mount


Clark and Lewis attend a ball in St. Louis that continues all night. The host hopes the U.S. Government will pay back the $622 the party cost him. At camp, Sgt. Ordway writes a letter to his parents.
May 16, 1804
St. Charles arrival


The boats set out early, pass the coal beds of Charbonier Bluff, and reach St. Charles, an early French settlement on the Missouri River. Many citizens come out to see the event and socialization commences.
May 20, 1804
Sunday in St. Charles


Lewis and a delegation of distinguished citizens leave St. Louis. During a thunderstorm, they shelter in a little cabin. Already in St. Charles, many of the enlisted men attend Catholic mass.
June 3, 1804
Mosquitoes and ticks


At the mouth of the Osage, mosquitoes and deer ticks vex Clark, and Lewis collects a specimen of ground plum. Late in the day, the boats move up to the mouth of the Moreau east of present Jefferson City.
June 12, 1804
Old Dorion signs on


Near present Dalton, Missouri, the expedition meets a contingent of boats led by fur trader Pierre Dorion, Sr. He agrees to join as an interpreter, and one expedition member is sent back to St. Louis.
October 29, 1804
Mandan-Hidatsa-Arikara peace


Ruptáre, second Mandan village, ND The standard diplomatic speech is given at a council with the Mandans and Hidatsas. The captains ask them to also smoke the pipe of peace with Arikara Chief Too Né. Medals, flags, and clothing are given as gifts.
March 24, 1805
Bird cages


At Fort Mandan, cages are made for the live birds that will soon be sent to Washington City. In St. Louis, Capt. Amos Stoddard updates President Thomas Jefferson regarding Lewis’s delegation of Iowas.
October 21, 1805
Columbia River rapids


Near John Day Dam, WA The paddlers navigate several rapids while the non-swimmers walk around them, something Clark says has become routine. They buy food and firewood from Indians who show “great kindness,” and Collins shares his home-brewed beer.
October 22, 1805
The Falls of the Columbia
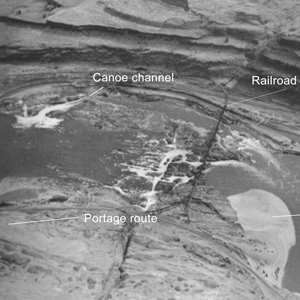

Celilo Falls, WA-OR After arriving at Celilo Falls, they carry their baggage along the river’s northern shore with the help of Wishram Indians. Others cross the river to scout the channel that the canoes must navigate. In Philadelphia, Peale cares for Lewis’s prairie dog and in St. Louis, an Indian delegation leaves for Washington City.
Notes
| ↑1 | Mark J. Wagner in Fort Kaskaskia citing Robert A. Stoddard, ed., The Autobiography Manuscript of Major Amos Stoddard (San Diego: Robert Stoddard Publishing, 2016), 48–51. |
|---|
